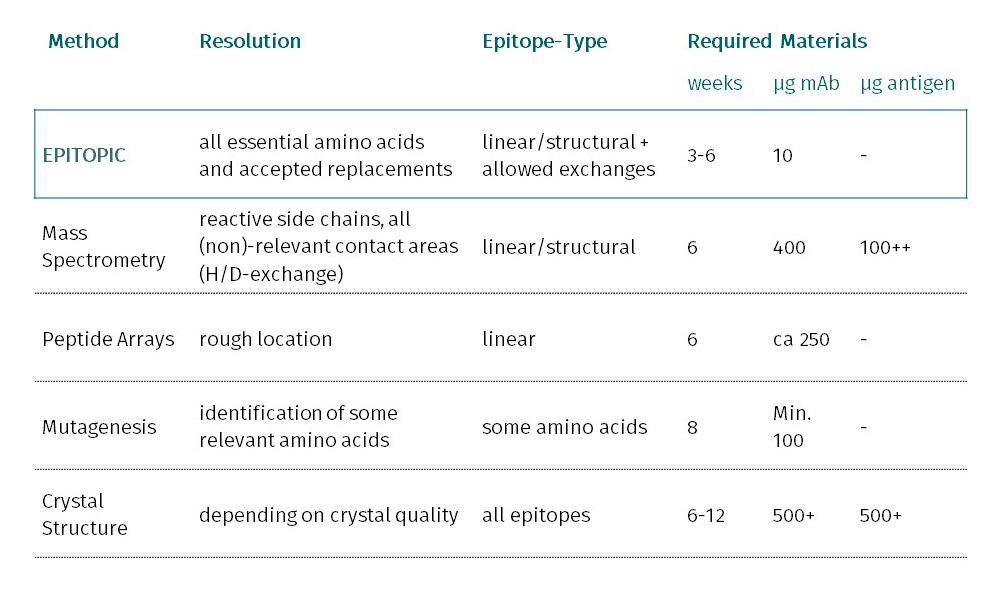
Epitopic’s epitope fingerprinting focuses on the rapid Identification of antibody epitopes by statistical means from a naïve library. For more information about our methods and approaches, please check the pages under Technologies.
Epitope mapping is the identification of antibody epitopes as part of a protein sequence or on the landscape of a protein structure. epitopic's epitope fingerprinting delivers in addition an insight into the allowed variations and structural features as they can only be obtained, when hundreds of different binding peptide variants are derived from a wet lab experiment.
Epitopic provides analyses of epitopes of mono/polyclonal antibodies, even in sera.
Discontinuous epitopes are usually not a problem, because we produce data beyond the normal output of an Ala-scan. “Structural” epitopes requiring special constraint structures, like those flanked by cysteine disulfide bridges or simply in ordinary loop structures are within the range of sequences favored in our libraries. “Structural” epitopes comprising conserved and short continuous stretches of amino acids have been identified in many cases.
In allergy projects at Fraunhofer IZI in Leipzig peptide arrays have been compared to epitope fingerprinting. The result was that the array missed all structural and even continuous epitopes discovered by the fingerprinting technology.
Our libraries are of unmatched diversity and epitopic is using a special software to exploit their special features. It took ten years and projects of all kinds to reach the present level.
a. Epitope sequence
b. Comparison of monoclonal antibodies
c. Identification of binding peptides for QC
d. Competing peptides with different affinities to the antibody for diagnostics
e. Binding peptides to predefined target structures
f. Patentability of an antibody
10-20 µg antibody is already perfect in most cases, purity usually does not matter. For mixtures like polyclonal serum please inquire regarding the details. Use our contact form to get in touch with us.
Quality is of importance with respect to the integrity of the antibody. Clean versus decomposed materials from the same mAb clone but different providers can result in dramatic differences in the precision an epitope can be defined. Which is obvious, when taking into account our everyday experiences with westernblots or ELISAs.
That is depending on the setup of the project/experiments. For one monoclonal Antibody the standard analysis takes around 2-3 weeks. For more antibodies, the time needed will increase, but usually not more than 4-6 weeks. For questions concerning your project idea, please use the contact form to get in touch with us.
The final report covers all epitopes of the delivered antibodies. The epitopes are usually defined at the amino acid level, a resolution otherwise only achieved by Ala-scan. The report includes sequences, alignments and a summary and analysis of the results. If there are more epitopes found, they will also be described or named in the report. For brief examples see here.
Usually, it is a twostep project:
a. In a first step selections are carried out and the resulting NGS-data is checked for matching QC-criteria. If the antibody is of limited quality and the QC is not passed, the customer will only pay the upfront fee covering this step.
b. In a second step, often in close exchange with the customer, the data is analyzed and further processed to identify the epitopes and, where necessary, peptides for all kinds of applications. See here.